What is a Computer Virus?
Computer viruses are malicious software programs designed to replicate themselves and spread from one computer to another. They are often attached to files, programs, or documents and can cause various types of damage to a computer system.
What is a Computer Virus?
A computer virus is a type of malware that infects a computer system by inserting its code into legitimate programs or files. When these infected files are executed or accessed, the virus activates and starts its malicious activities, which can include:
1. Replication:-
Viruses can replicate themselves by attaching their code to other files or programs. This allows them to spread to other computers via infected files, networks, or removable storage devices.
2. Data Corruption:-
Some viruses are designed to corrupt or delete data on the infected computer. This can cause loss of important files, documents, or even system files crucial for the operating system's functionality.
3. Unauthorized Access:-
Certain viruses create backdoors or penetrability in a system, allowing hackers to gain unauthorized access. This can lead to identity theft, unauthorized control of the system, or espionage.
4. Spying and Monitoring:-
Some viruses are programmed to spy on users' activities, capturing keystrokes, stealing sensitive information (such as passwords or credit card details), or monitoring browsing habits.
Types of Computer Viruses:
1. File Infector Viruses:-
- These viruses attach themselves to executable files (such as .exe or .dll files). When the infected file is executed, the virus activates and spreads by infecting other files.
2. Boot Sector Viruses:-
- Boot sector viruses infect the master boot record (MBR) or boot sector of a hard drive or removable storage. They activate when the system boots up, allowing the virus to load into memory before the operating system.
3. Macro Viruses:-
- These viruses infect documents that support macros (e.g., Microsoft Word, Excel). They embed malicious code into macros and execute when the infected document is opened.
4. Polymorphic Viruses:-
Polymorphic viruses can change their code or appearance to evade detection by antivirus software. They modify themselves each time they infect a new file or system.
5. Resident Viruses:-
- Resident viruses embed themselves in a computer's memory and can infect files or systems whenever certain actions are performed (e.g., file access, file creation).
6. Multipartite Viruses:-
- These viruses combine characteristics of multiple virus types. They can infect both files and the boot sectors of a computer.
7.Worms:-
- While not strictly viruses, worms are a type of self-replicating malware that spreads across networks, often exploiting vulnerabilities in network protocols or operating systems.
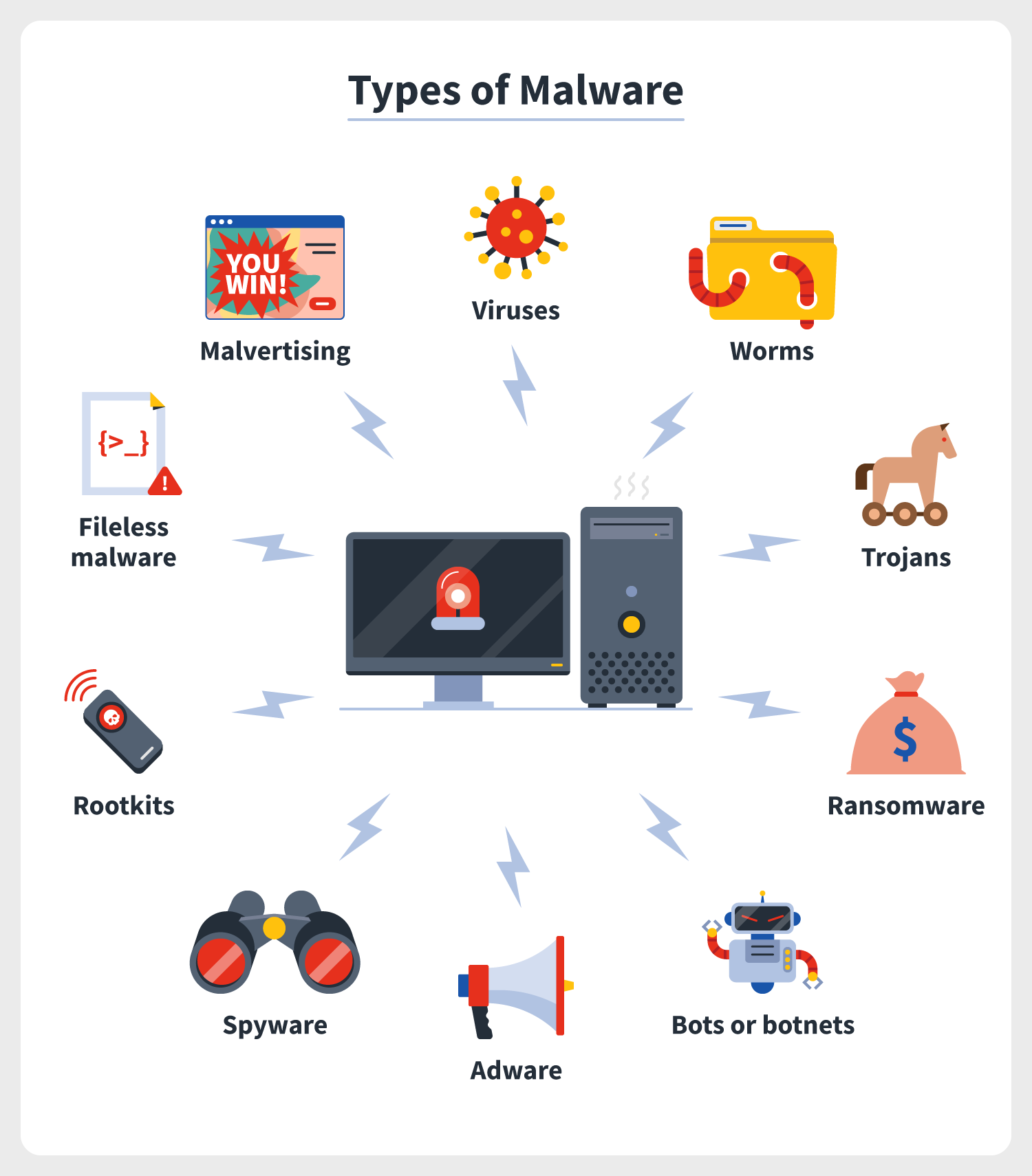
Understanding these types of viruses can help users and cybersecurity professionals identify and mitigate potential threats. Regularly updating antivirus software, practicing safe browsing habits, and being cautious with file downloads can help protect against these malicious programs.