Identity the peripherals of computer components in CPU and its functions.
Task 2: - Identity the peripherals of computer components in CPU and its functions.
Computer System-
A computer system consists of hardware components that have been carefully chosen so that they work well Together and software components or programs that run in the computer. The main software component is itself an operating system (OS) that manages and provides services to other Programs that can be run in the computer.

CPU (Central Processing Unit) components and peripherals devices
The CPU, monitor, UPS, keyboard, and mouse are examples of hardware. These are the components that make up a computer’s hardware. Peripheral hardware includes Graphical card, external hard drives, pen drives, USB, and other devices. These are referred to as “peripherals hardware.”
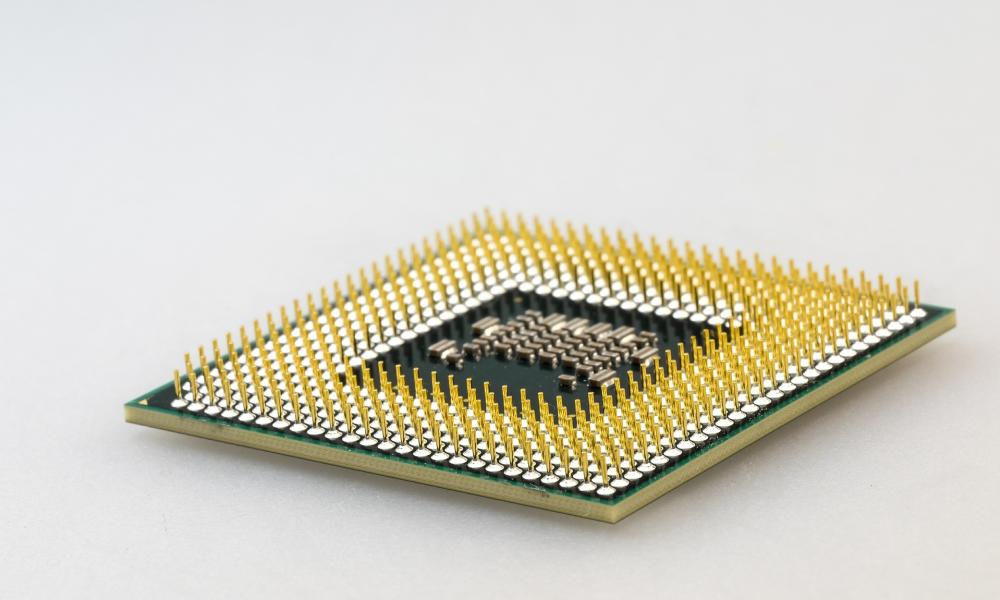
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
A central processing unit (CPU) - also called a central processor or main processor –is the most important processor in a given computer its electronic circuitry executes instructions of a computer program, such as arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input output (I/O) operations.

Peripheral Device
A peripheral device is an internal or external device that connects directly to a computer or other digital device but does not contribute to the computer’s primary function, such as computing. It helps and users and use the functionalities of a computer.

INPUT –
In computing, an input device is a piece of equipment used to provide data and control signals to an information processing system, such as a computer or information appliance. Example of input devices includes keyboard, mouse, scanners, cameras, joysticks, and microphones.
OUTPUT-
An output device is any piece of computer hardware that converts information into a humanperceptible form or, historically, into a physical machine-readable form for use with other non-computerized equipment. It can be text, graphics, tactile, audio or video.
I/O DEVICES-
Alternatively called and IO device, an input/output device is hardware a human operator or other systems uses to communicate with a computer. As the name suggests, input/output devices can send data (output) to a computer and receive data from a computer (input).

(A)The Motherboard various component inside motherboard
I. Mouse/Keyboard-
Mouse is a hand operated pointing device. When you move the mouse on your desk, the mouse pointer on the screen mimics its movement. Keyboard a panel of keys used for putting information including letters, words, and numbers into your computer.

II. USB-
Universal Series Bus (USB) is an industry standard that specifies the physical interfaces and protocols for connecting, data transferring and powering of hosts, such as personal computer, peripherals, e. g. keyboard and mobile devices, and intermediate hubs.

III. CPU CHIP-
The CPU is seen as the main and most crucial integrated circuitry (IC) chip in a computer, as it is responsible for interpreting most of computer’s commands.
IV. RAM SLOT-
A memory slot is responsible for temporarily storing data in a computer’s RAM (Random Access Memory), a type of volatile memory that allows data quickly.

V. Floppy Controller-
A floppy disk controller (FDC) is a specially designed chip that controls the reading and writing functionality of a floppy drive.

VI. PCI Slot-
A PCI slot is a built-in slot on a device that allows for the attachment of various hardware components such as network cards, modems, sound cards, disk controllers and other peripherals.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/pci-express-pcie-2625962-79f643e7768d4b8e81e2eee6cf5b02e7.png)
VII. ISA Slot-
Short for Industry Standard Architecture, ISA was introduced by IBM and headed by Mark Dean. ISA was originally an 8-bit computer bus that was later expanded to a 16-bit bus in 1984. When this bus was originally released, it was a proprietary bus, which allowed only IBM to create peripherals and the actual interface. However, in the early 1980s, other manufacturers were creating the bus.

VIII. CMOS Battery-
The CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) battery on your computer's motherboard acts as an emergency power for the BIOS and date and time settings. The CMOS keeps those BIOS or UEFI settings stored in CMOS RAM when your computer doesn't receive any external power, e.g., when the PSU is disconnected.

IX. AGP Slot-
Short for accelerated graphics port, AGP is an advanced port designed for video cards and 3D accelerators. Developed by Intel and introduced in August 1997, AGP introduces a dedicated point-to-point channel that allows the graphics controller direct access to the system memory.

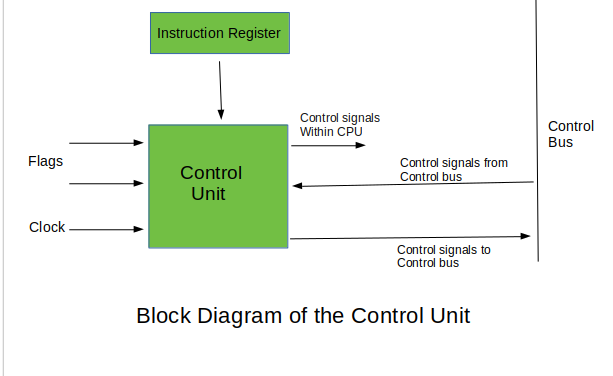
2.Control Unit-
CU stands for Control Unit. It is one of the fundamental parts of the CPU. The main work of the CU is to tell the most efficient method to work. It guides all the related operations to the individual parts of the processor.
3.ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit)-
In the computer system, ALU is a main component of the central processing unit, which stands for arithmetic logic unit and performs arithmetic and logic operations.

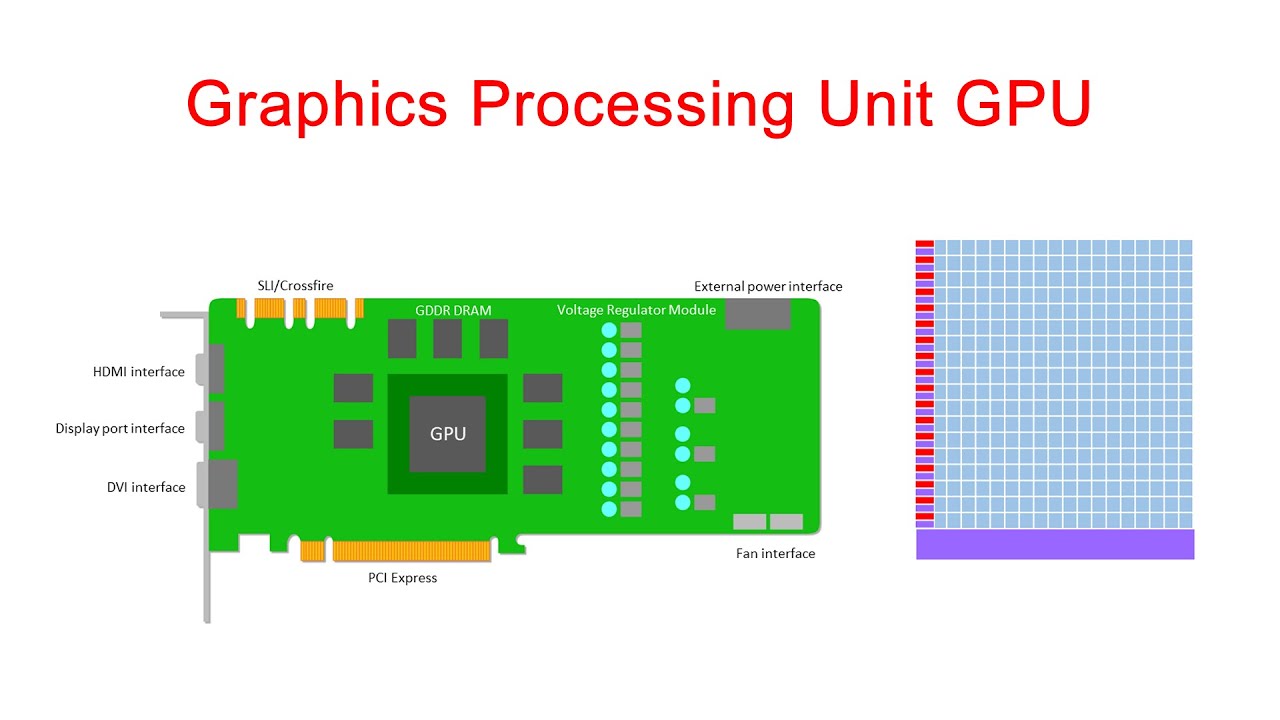
4.GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) -
The easiest way to understand what a GPU does is to talk about video games. In a game, we might see a computer-generated image of a person, a landscape, or an intricately detailed model of a 3D object. Whatever it is we're seeing, it's all thanks to the graphics processing unit.
5.STORAGE-
Data storage is the collective methods and technologies that capture and retain digital information on electromagnetic, optical or silicon-based storage media.

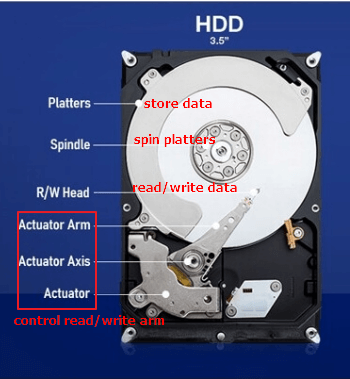
6. HDD (Hard Disk Drive) -
A hard drive or hard disk drive (HDD) is a type of data storage device that is used in laptop and desktop computers.
8. SSD (Solid State Drive) -
A solid –state drive (SSD) is a new generation of storage device used in computers. SSDs store data using flash –based memory, which is much faster than the traditional hard disks they’ve come to replace.
